Importing and visualising EEG data
Below we import and reshape EEG data from the eegkit package.
library(neurogam)
library(ggplot2)
library(eegkit)
library(dplyr)
# retrieving some EEG data
data(eegdata)
head(eegdata)
#> subject group condition trial channel time voltage
#> 1 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 0 -8.921
#> 2 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 1 -8.433
#> 3 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 2 -2.574
#> 4 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 3 5.239
#> 5 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 4 11.587
#> 6 co2a0000364 a S1 0 FP1 5 14.028
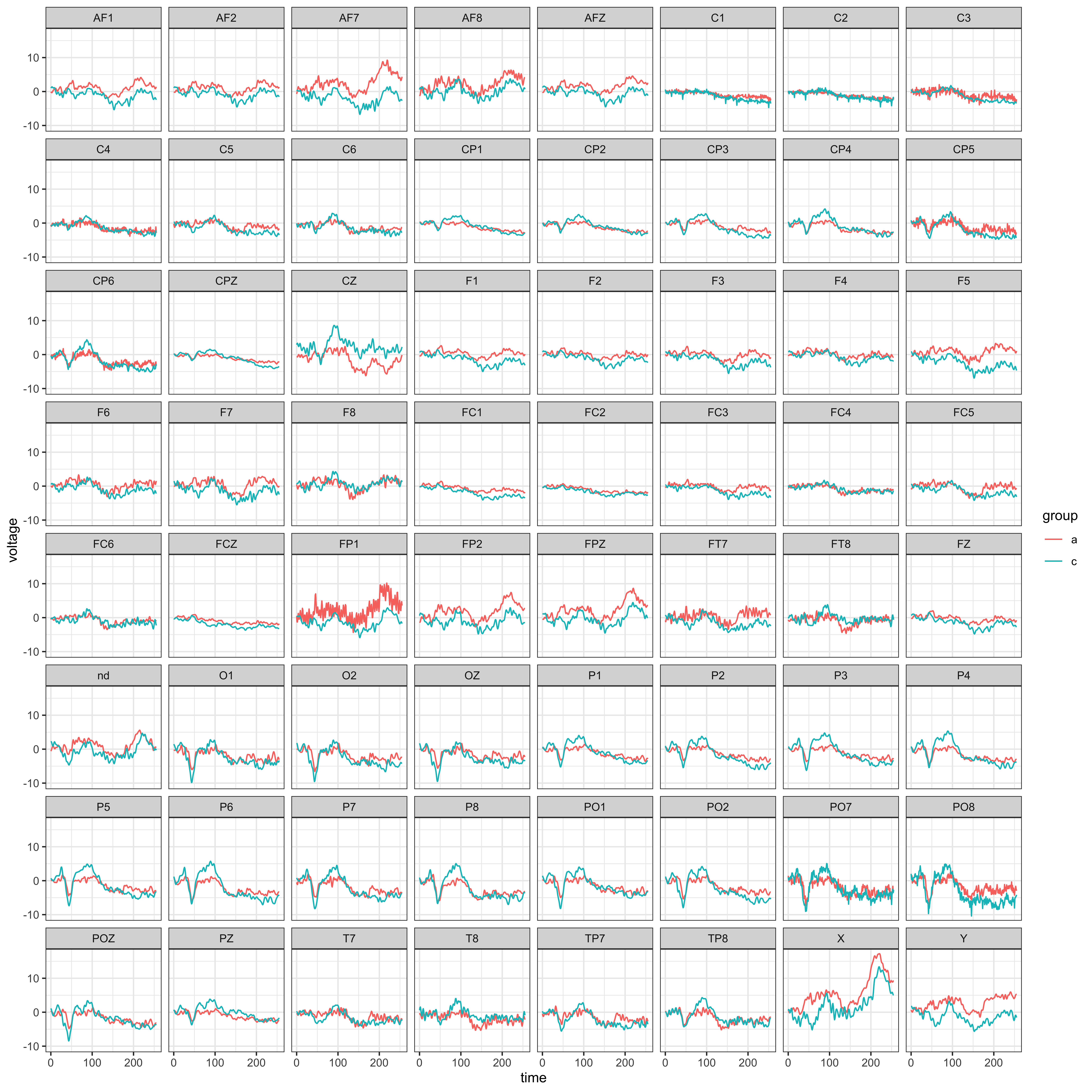
# plotting the average ERP per group and channel
eegdata |>
summarise(voltage = mean(voltage), .by = c(group, channel, time) ) |>
ggplot(aes(x = time, y = voltage, colour = group) ) +
geom_line() +
facet_wrap(~channel) +
theme_bw()
# reshape the data
eeg_data <- eegdata |>
# keeping only one channel
dplyr::filter(channel == "PZ") |>
# converting timesteps to seconds
mutate(time = (time + 1) / 256) |>
# rounding numeric variables
mutate(across(where(is.numeric), ~ round(.x, 4) ) ) |>
# removing NAs
na.omit()
# show a few rows
head(eeg_data)
#> subject group condition trial channel time voltage
#> 1 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0039 -2.797
#> 2 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0078 -4.262
#> 3 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0117 -4.262
#> 4 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0156 -2.797
#> 5 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0195 -0.844
#> 6 co2a0000364 a S1 0 PZ 0.0234 0.132
Fitting the model
We fit the model (a BGAMM) on one channel (PZ) to test for group difference at every timestep.
# fitting the BGAMM to identify clusters (around 30 min on 4 parallel apple M4 cores)
results <- testing_through_time(
# EEG data
data = eeg_data,
# participant column
participant_id = "subject",
# EEG column
outcome_id = "voltage",
# name of predictor in data
predictor_id = "group",
# basis dimension
kvalue = 40,
# we recommend fitting the GAMM on summary statistics (mean and SD)
multilevel = "summary",
# threshold on posterior odds
threshold = 10,
# number of MCMCs
chains = 4,
# number of parallel cores
cores = 4
)
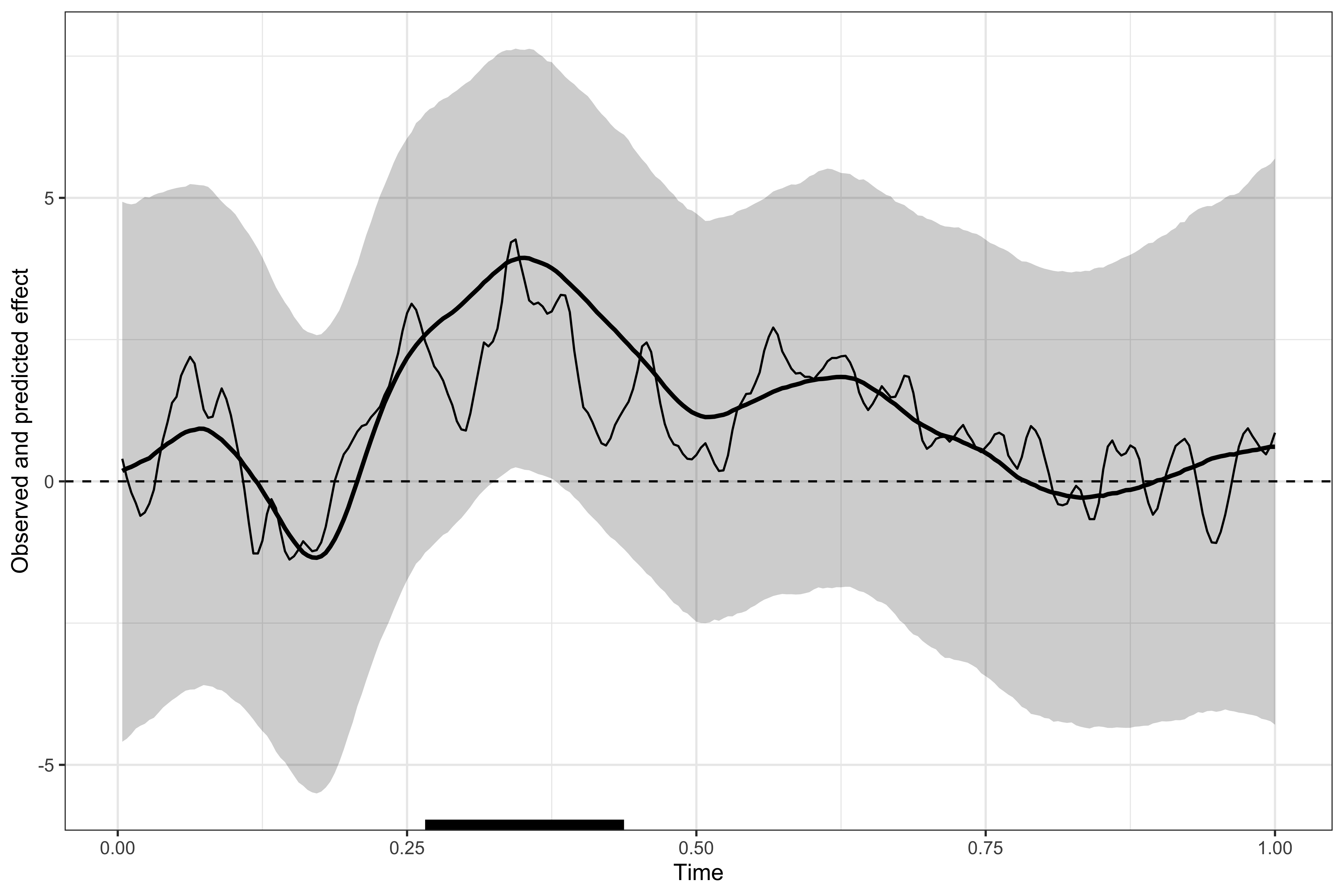
Visualising the results
# displaying the identified clusters
print(results)
#>
#> ==== Time-resolved GAMM results ===============================
#>
#> Clusters found:
#>
#> sign id onset offset duration
#> positive 1 0.266 0.438 0.172
#>
#> =================================================================
# plotting the data, model's predictions, and clusters
plot(results)
Computing clusters at the participant-level
Below we fit a new model, specifying predictor_id = NA (because group varies across participants) and by_ppt = TRUE to test whether EEG amplitude (voltage) differs from 0 and return clusters at the participant level.
# fitting the BGAMM to identify clusters (around 30 min on 4 parallel apple M4 cores)
results <- testing_through_time(
# EEG data
data = eeg_data,
# participant column
participant_id = "subject",
# EEG column
outcome_id = "voltage",
# here we use no predictor (because group varies across participants)
predictor_id = NA,
# basis dimension (for both the group and participant levels)
kvalue = 40,
# we recommend fitting the GAMM with summary statistics (mean and SD)
multilevel = "summary",
# return clusters at both the group and participant levels
by_ppt = TRUE,
# threshold on posterior odds
threshold = 10,
# number of MCMCs
chains = 4,
# number of parallel cores
cores = 4
)
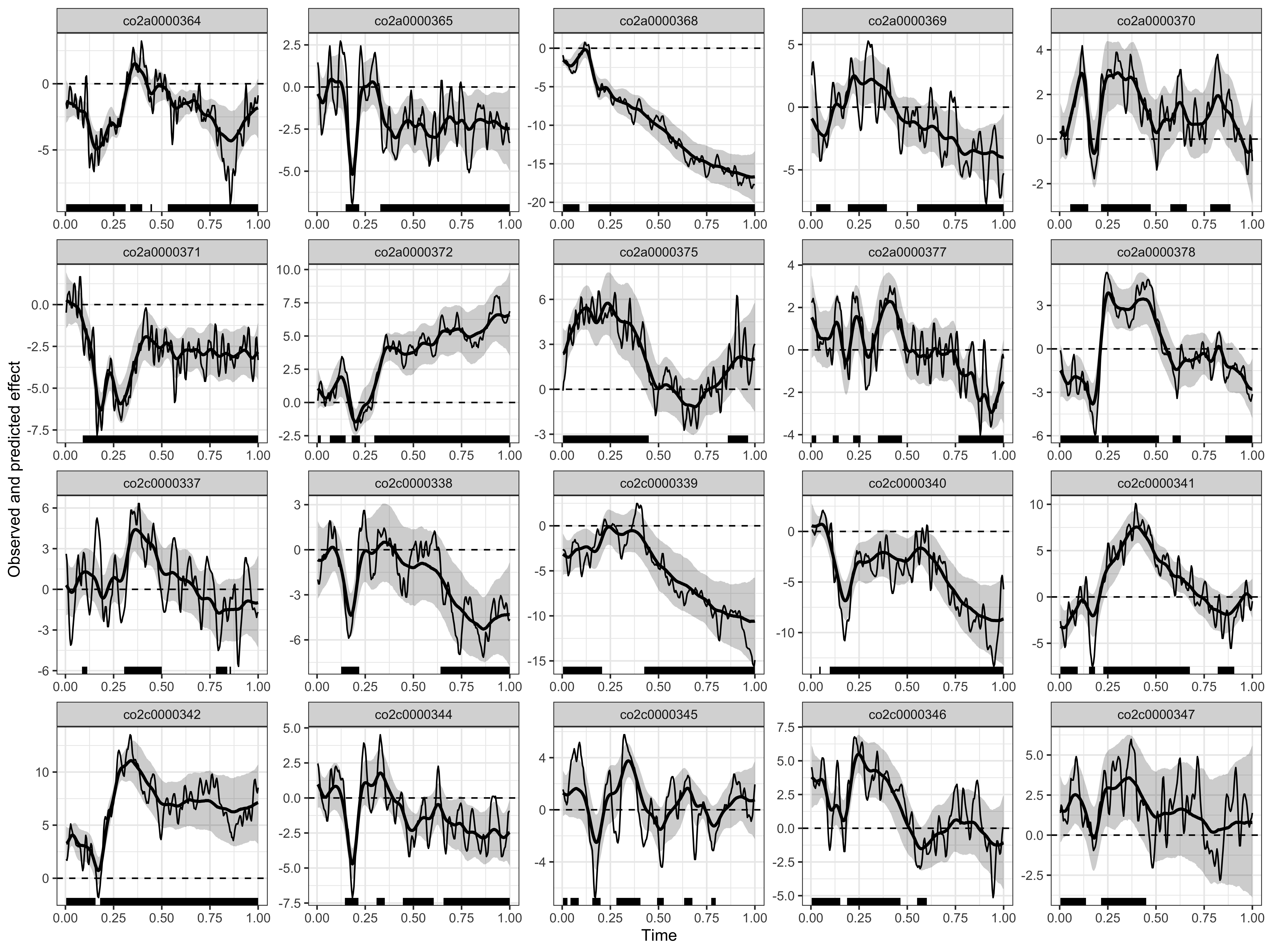
Visualising the results
# displaying the identified clusters
print(results)
#>
#> ==== Time-resolved GAMM results ===============================
#>
#> Clusters found:
#>
#> participant sign id onset offset duration
#> co2a0000364 positive 1 0.336 0.398 0.062
#> co2a0000364 negative 1 0.004 0.312 0.308
#> co2a0000364 negative 2 0.441 0.449 0.008
#> co2a0000364 negative 3 0.531 1.000 0.469
#> co2a0000365 negative 1 0.148 0.219 0.071
#> co2a0000365 negative 2 0.328 1.000 0.672
#> co2a0000368 negative 1 0.004 0.090 0.086
#> co2a0000368 negative 2 0.137 1.000 0.863
#> co2a0000369 positive 1 0.191 0.394 0.203
#> co2a0000369 negative 1 0.027 0.102 0.075
#> co2a0000369 negative 2 0.551 1.000 0.449
#> co2a0000370 positive 1 0.055 0.148 0.093
#> co2a0000370 positive 2 0.215 0.473 0.258
#> co2a0000370 positive 3 0.574 0.660 0.086
#> co2a0000370 positive 4 0.781 0.887 0.106
#> co2a0000371 negative 1 0.090 1.000 0.910
#> co2a0000372 positive 1 0.004 0.020 0.016
#> co2a0000372 positive 2 0.066 0.148 0.082
#> co2a0000372 positive 3 0.297 1.000 0.703
#> co2a0000372 negative 1 0.180 0.223 0.043
#> co2a0000375 positive 1 0.004 0.449 0.445
#> co2a0000375 positive 2 0.859 0.965 0.106
#> co2a0000377 positive 1 0.004 0.027 0.023
#> co2a0000377 positive 2 0.113 0.144 0.031
#> co2a0000377 positive 3 0.219 0.258 0.039
#> co2a0000377 positive 4 0.348 0.473 0.125
#> co2a0000377 negative 1 0.766 1.000 0.234
#> co2a0000378 positive 1 0.219 0.516 0.297
#> co2a0000378 negative 1 0.004 0.203 0.199
#> co2a0000378 negative 2 0.586 0.629 0.043
#> co2a0000378 negative 3 0.789 0.789 0.000
#> co2a0000378 negative 4 0.859 1.000 0.141
#> co2c0000337 positive 1 0.086 0.113 0.027
#> co2c0000337 positive 2 0.305 0.500 0.195
#> co2c0000337 negative 1 0.781 0.840 0.059
#> co2c0000337 negative 2 0.852 0.859 0.007
#> co2c0000338 negative 1 0.125 0.219 0.094
#> co2c0000338 negative 2 0.641 1.000 0.359
#> co2c0000339 negative 1 0.004 0.207 0.203
#> co2c0000339 negative 2 0.426 1.000 0.574
#> co2c0000340 positive 1 0.043 0.051 0.008
#> co2c0000340 negative 1 0.098 1.000 0.902
#> co2c0000341 positive 1 0.227 0.676 0.449
#> co2c0000341 negative 1 0.004 0.094 0.090
#> co2c0000341 negative 2 0.152 0.184 0.032
#> co2c0000341 negative 3 0.820 0.906 0.086
#> co2c0000342 positive 1 0.004 0.156 0.152
#> co2c0000342 positive 2 0.180 1.000 0.820
#> co2c0000344 positive 1 0.246 0.246 0.000
#> co2c0000344 positive 2 0.309 0.352 0.043
#> co2c0000344 negative 1 0.144 0.215 0.071
#> co2c0000344 negative 2 0.445 0.606 0.161
#> co2c0000344 negative 3 0.656 1.000 0.344
#> co2c0000345 positive 1 0.004 0.027 0.023
#> co2c0000345 positive 2 0.043 0.086 0.043
#> co2c0000345 positive 3 0.281 0.406 0.125
#> co2c0000345 positive 4 0.633 0.676 0.043
#> co2c0000345 negative 1 0.156 0.199 0.043
#> co2c0000345 negative 2 0.492 0.527 0.035
#> co2c0000345 negative 3 0.773 0.797 0.024
#> co2c0000346 positive 1 0.004 0.152 0.148
#> co2c0000346 positive 2 0.188 0.465 0.277
#> co2c0000346 negative 1 0.551 0.602 0.051
#> co2c0000347 positive 1 0.004 0.137 0.133
#> co2c0000347 positive 2 0.215 0.449 0.234
#>
#> =================================================================
# plotting the data, model's predictions, and clusters
plot(results)
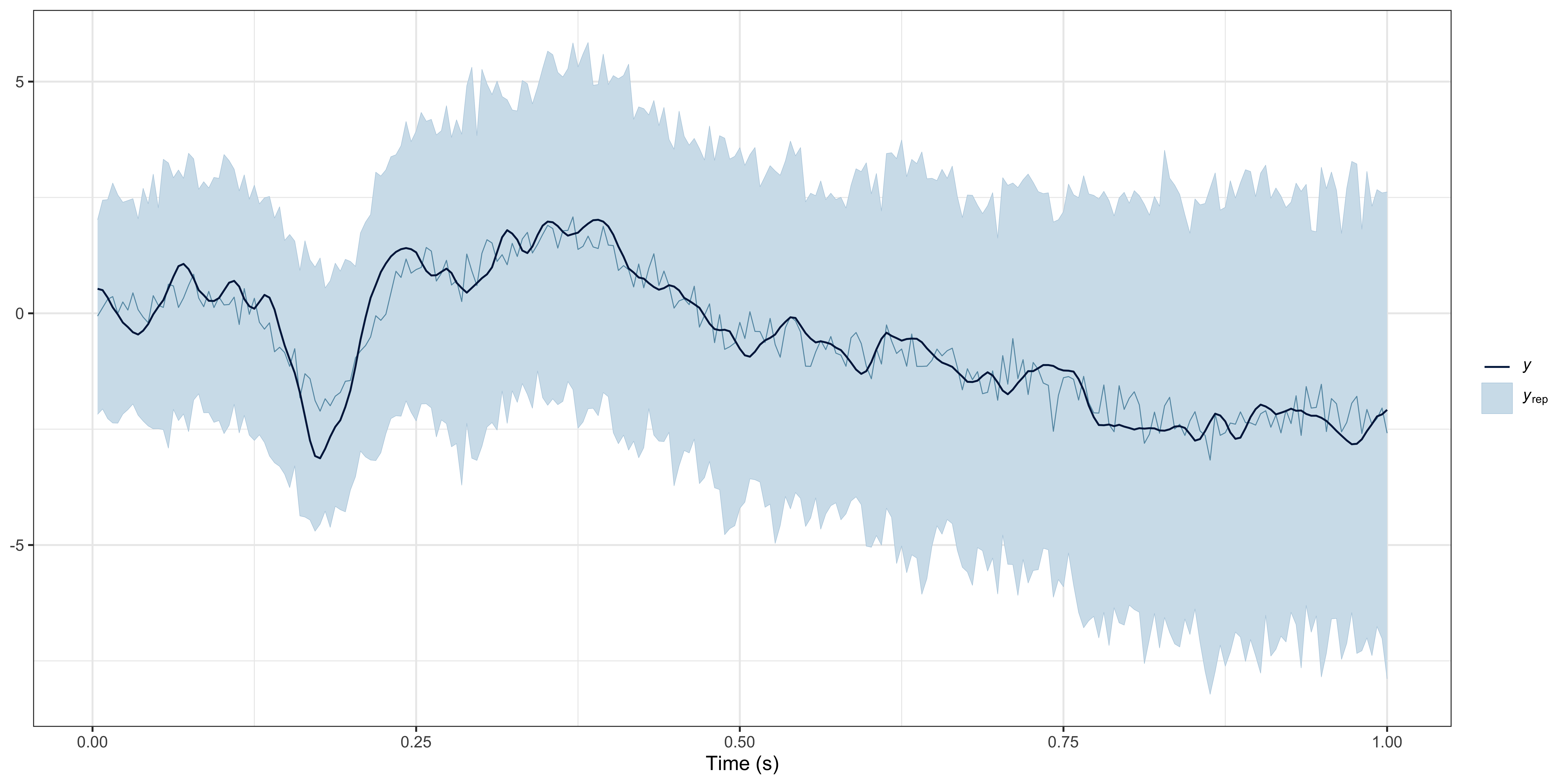
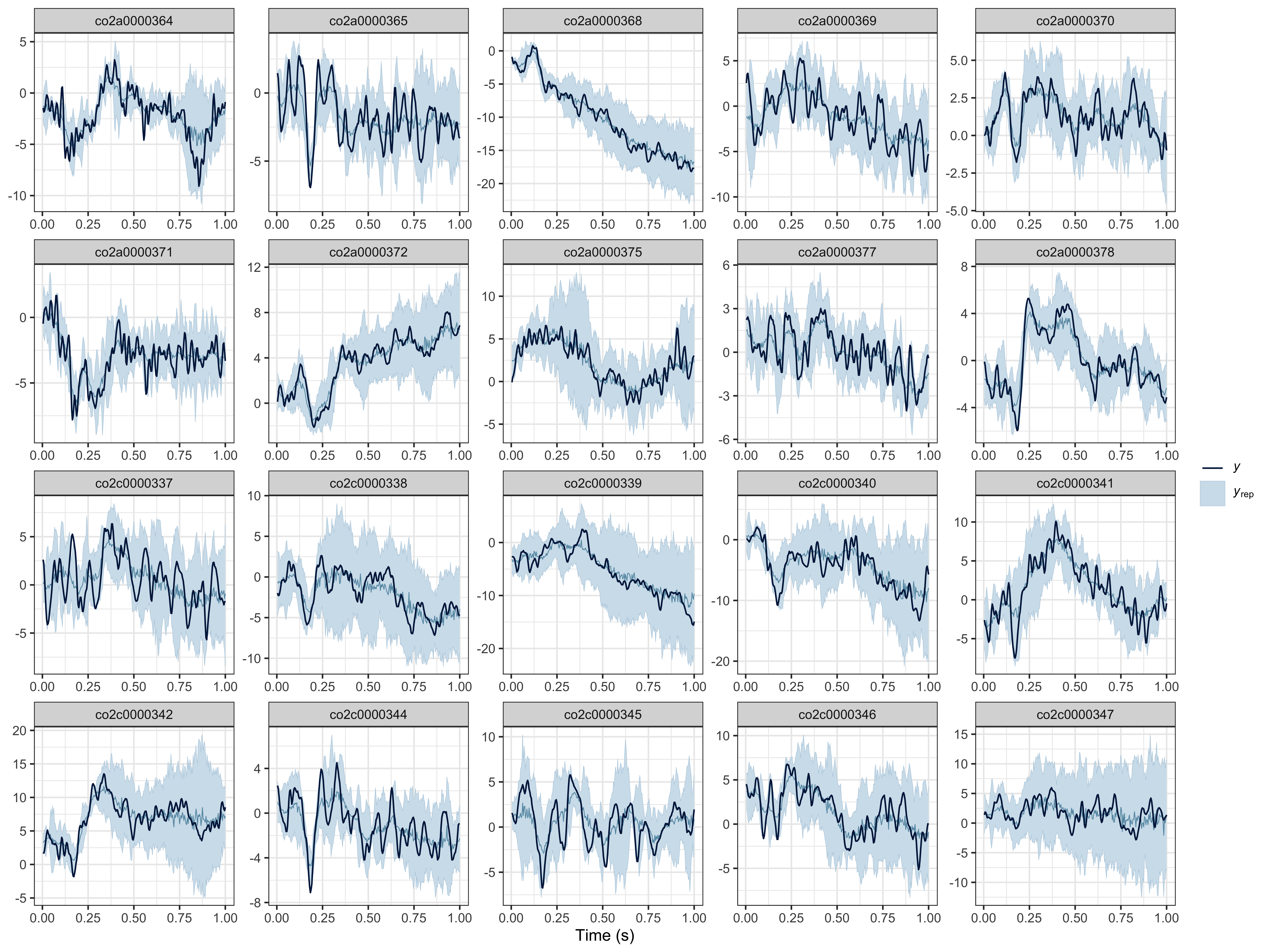
Posterior predictive checks
We recommend visually assessing the predictions of the model against the observed data (for each participant). We provide a lightweight ppc() method, but you can conduct various PPCs with brms::pp_check(results$model, ...) (for all available PPCs, see https://mc-stan.org/bayesplot/reference/PPC-overview.html).
# posterior predictive checks (PPCs) at the group level
ppc(object = results, ppc_type = "group")
# posterior predictive checks (PPCs) at the participant level
ppc(object = results, ppc_type = "participant")